Thursday, June 24, 2010
=IF() Function
Syntex : "=IF(Condition,TRUE,FALSE)"
The Excel IF() checks to see if a certain condition is true or false. If the condition is satisfied then it returns true, else retun false.
The IF() we are using in this tutorial will asks if the value in column A is greater than the value in column B. If the condition get true then it will show value as "A is larger" in column D. If it is not, the IF function will place the statement "B is larger" in column D.
Add some value to Cell A1 and Cell B1 and write following formula in Cell D1.
=IF(A1 > B1,"A is larger","B is larger")
Note: There are two text statements "A is larger" and "B is larger" are in quotations. In order to add text to an Excel IF Function, it must be in quotation marks.
How to write Multiple IF function ?
From above example, if we want to check for 3 different value, we have to use multiple if function... Let's C how can we do it.
example with value :
Cell A1 =5
Place formula at Cell B1
=IF(A1=5,"Five",IF(A1=10,"Ten","Unknown Value"))
In above examples we check for the value in Cell A1, If it contains value 5 then in Cell B1 you will get "Five", in case if you now change value in Cell A1 to 10 then In Cell B1 it will automatically reflect as "Ten" and other this two value will show "Unknown Value".
As I told you IF check for the Condition and work accordingly, when we have wrote "=IF(A1=5," is the condition check point TRUE="Five", FALSE = IF(A1=10,"Ten","Unknown Value"). when we have written again IF condition in the IF that means it again going to check for condition and will return to parent function either TRUE or FALSE.
About macros in Excel
Recording macros
Making a macro easy to run
Managing your macros
Macro security
Wednesday, June 23, 2010
Check your Anti Virus is Working or Not?
Just you have to follow simple instructions....
# open Notepad application and save following string as it is. this string is 68 character long
X50!P%@AP[4\PZX54(P^)7CC)7}EICAR-STANDARD-ANTIVIRUS-TEST-FILE!$H+H*
Save this file as eicar.com, if your anti-virus software stop you, then it your anti-virus softwares is doing good. Its not harmful either but if the anti virus is active it will warn you. if it does not then your anti virus is good for nothing.
For more your can check out EICAR web site
Friday, June 11, 2010
IBM Lotus Symphony
IBM Lotus Symphony is a application suite for creating, editing, and sharing text, spreadsheet, presentations and other documents, and is currently distributed as freeware.
Lotus Symphony supports platforms for Microsoft Windows, Linux and Mac OS.
Symphony consists:
- IBM Lotus Symphony Documents, (A Word Processor)
- IBM Lotus Symphony Spreadsheets,(A Spreadsheet application)
- IBM Lotus Symphony Presentations, (A Presentation application)
Document Application:
Lotus Symphony Documents supports .doc (Microsoft), .dot (Microsoft template), .docx (Microsoft Word 2007), .dotx (Microsoft Word 2007 template),.odt (ODF), .ott (ODF template), .sxw (OpenOffice.org 1.1 format), .stw (OpenOffice.org 1.1 format template), .lwp (IBM Lotus SmartSuite®), .mwp (IBM Lotus SmartSuite template), .rtf, and .txt formats
Spreadsheet Application:

Lotus Symphony Spreadsheets supports .xls (Microsoft), .xlt (Microsoft template), .xlsx (Microsoft Excel 2007), .xltx (Microsoft Excel 2007 template), .ods (ODF), .ots (ODF template), .sxc (OpenOffice.org 1.1 format), .stc (OpenOffice.org 1.1 format template), .123 (IBM Lotus Smartsuite), .12m (IBM Lotus Smartsuite template), .xml, and .csv formats
Presentation Application:

Lotus Symphony Presentations supports .ppt (Microsoft), .pot (Microsoft template), .pptx (Microsoft PowerPoint 2007), .potx (Microsoft PowerPoint 2007 template), .odp (ODF), .otp (ODF template), .prz (IBM Lotus Smartsuite), .mas (IBM Lotus Smartsuite look template), .smc (IBM Lotus Smartsuite content template), .sxi (OpenOffice.org 1.1 format), and .sti (OpenOffice.org 1.1 format template)formats.
Get more Information about symphony
Thursday, June 3, 2010
Cloud Computing
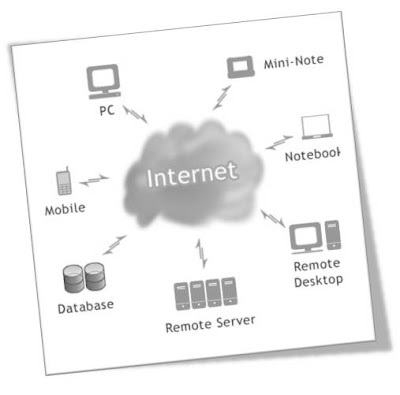
What Is Cloud Computing? Now a days I have found number of people are talking about Cloud computing. In the business world are also asking the same question, "What is Cloud Computing, and what does it mean for a business?" Cloud computing platforms are growing in popularity day by day, but why? What unique advantages does a cloud computing architecture offer to companies in today’s economic climate? Let’s explore the cloud computing infrastructure and its impact on critically important areas to IT, like security, infrastructure investments, business application development, and more. Most IT departments are forced to spend a significant portion of their time on frustrating implementation, maintenance, and upgrade projects that too often don’t add significant value to the company’s bottom line. Increasingly, IT teams are turning to cloud computing technology to minimize the time spent on lower-value activities and allow IT to focus on strategic activities with greater impact on the business. The fundamental benefits delivered by cloud computing technology.
- Web-services integration. Cloud computing technology is much easier and quicker to integrate with your other enterprise applications (both traditional software and cloud computing infrastructure-based), whether third-party or homegrown.
- A 100% cloud computing infrastructure does not need hardware or software to install. In fact it just requires significantly fewer capital expenditures to get up and running.
- Your cloud computing technology applications are live in a matter of weeks or months, even with extensive customization or integration. So, it is faster and lower-risk deployment.
- Cloud computing technology is ideal for application development to support your organization’s evolving needs and it is not difficult or impossible to customize.
- Cloud computing techology do everything for the business users that can help them to do customization, report, etc.
- As Cloud computing technology doesn’t force you to decide between upgrading and preserving all your hard work, because those customizations and integrations are automatically preserved during an upgrade.
- The Force.com AppExchange features hundreds of applications built for cloud computing infrastructure, pre-integrated with your Salesforce CRM application or your other application development work on Force.com.
- Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
- Google App Engine
- Force.com
- GoGrid
- Azure
- Intuit Partner Platform (IPP)
Refrence link
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computing
Windows Management Instrumentation Command
Read a huge range of information about local or remote computers. Also provides a way to make configuration changes to multiple remote machines.
Syntax
WMIC [global switches] [/locale:ms_409] alias> [options][format]
What is WMIC?
WMIC extends WMI for operation from several command-line interfaces and through batch scripts. Before WMIC, people used WMI-based applications (such as SMS), the WMI Scripting API, or tools such as CIM Studio to manage WMI-enabled computers. Without a firm grasp on a programming language such as C++ or a scripting language such as VBScript and a basic understanding of the WMI namespace, do-it-yourself systems management with WMI was difficult. WMIC changes this situation by giving you a powerful, user-friendly interface to the WMI namespace.
WMIC is more intuitive than WMI, in large part because of aliases. Aliases take simple commands that you enter at the command line, then act upon the WMI namespace in a predefined way, such as constructing a complex WMI Query Language (WQL) command from a simple WMIC alias Get command. Thus, aliases act as friendly syntax intermediaries between you and the namespace. For example, when you run a simple WMIC command such as
useraccount list brief
from the WMIC command prompt to get user account information, the Useraccount alias performs a WQL query of the Win32_Useraccount class and displays specific data from this class in text format. WMIC also displays the Win32_Useraccount class's properties at the console in text format. WMIC can return the results of a command in other formats, such as XML, HTML, and Comma Separated Value (CSV).
How to Run WMIC
To invoke the WMIC command prompt, type
wmic
in the standard XP or .NET Server command interpreter (cmd.exe), a Telnet session, or the Run dialog box. These startup methods are available locally or through a .NET Server Terminal Services session.
The first time you start WMIC, Windows installs it on the computer and displays the WMIC command prompt, wmic:root\cli>. At this prompt, you enter commands interactively. For example, the command
process where name='outlook.exe' call terminate
closes Microsoft Outlook if it's running. After the command runs, the WMIC command prompt reappears. Note that you must type each command in this article on one line, not split across multiple lines, for the commands to run properly. (Some commands in the tables and listings in this article are split across multiple lines for publication purposes.)
WMIC also runs in noninteractive mode. This mode is especially useful when you need to complete a single task or you need to run WMIC commands in a batch file. To run a command in noninteractive mode, you start WMIC and run the command in the same line of code. For example, you can open a command prompt and type
wmic /node:SERVER1 printer list status
to check the status of printers attached to SERVER1. In this example, WMIC starts, uses the /node switch to establish a remote connection to SERVER1, and runs a command to display printer status information. After the command runs and displays results, the command prompt reappears.
You can remotely access any WMI-enabled computer from any computer running WMIC. The computer you want to access doesn't require WMIC. For example, you can start WMIC from a computer running XP Professional Edition to manage a mix of computers running XP, Win2K, Windows NT 4.0, Windows Me, and Windows 9x.
WMIC Command-Line Components
WMIC uses global switches, aliases, verbs, commands, and command-line help to empower the interface. Global switches are settings that apply to and for the entire WMIC session. For example, the /trace:on switch enables error tracing. While this switch is on, WMIC returns error information for every command you execute. The /node switch lets you access a remote computer. The /interactive:on switch ensures that WMIC prompts you for confirmation before performing delete operations. Other global switches include /role, /user, /implevel, and /namespace.
Reference link
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/Aa394572
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa394531%28VS.85%29.aspx
http://support.microsoft.com/servicedesks/webcasts/wc072402/listofsampleusage.asp
http://ss64.com/nt/wmic.html

